Cnc Lathe Programming Manual
Programming is a fundamental skill for all types of CNC machining, even as automation and new technology seem to be replacing programming tasks. Every machinist still needs to understand how their programs and tools work. Whether you’re new to CNC programming and its most common language, g-code, or you’ve been writing code by scratch for years, CNC codes can still feel like a foreign language. And to make things worse, every machine speaks a different dialect you have to understand. Do you understand what they’re saying? Here are the g-code basics you need to know to efficiently understand and write programs that produce high quality products.
What is G-Code?
G-code is a programming language for CNC that instructs machines where and how to move. Most machines speak a different “dialect” of g-code, so the codes vary depending on type, make, and model. Each machine comes with an instruction manual that shows that particular machine’s code for a specific function.
Combination Manual Cnc Lathe
CNC Lathe Programming for Turning CNCCookbook’s G-Code Tutorial CNC Lathe Axes. CNC Lathes come in a variety of configurations, but for the basics, we’ll stick to the simplest and most common setup–2 axes.
- The basic CNC programming and the Difference between absolute programming mode and incremental programming mode is explained in this tutorial for Engineering Student as well as for beginners.
- The HAAS C.N.C. In a “CNC” (Computerized Numerical Control) machine, the tool is controlled by a computer and is programmed with a machine code system that enables it to be operated with minimal supervision and with a great deal of repeatability. The same principles used in operating a manual machine are used in programming a CNC.
G-code stands for “geometric code,” and follows some variation of the alpha numeric pattern:
N## G## X## Y## Z## F## S## T## M##
N: Line number
G: Motion
X: Horizontal position
Y: Vertical position
Z: Depth
F: Feed rate
S: Spindle speed
T: Tool selection
M: Miscellaneous functions
I and J: Incremental center of an arc
R: Radius of an arc
Alpha numeric codes are used for programming as they are a simple way to:
- Define motion and function (G##)
- Declare a position (X## Y## Z##)
- Set a value (F## and/or S##)
- Select an item (T##)
- Switch something on and off (M##), such as coolant, spindles, indexing motion, axes locks, etc.
For example,
G01 X1 Y1 F20 T01 M03 S500
would generally indicate a linear feed move (G01) to the given XY position at feed rate of 20. It is using Tool 1, and the spindle speed is 500. Miscellaneous functions will vary from machine to machine, so in order to know what the m-code means, the machine’s instruction manual will need to be referenced.
Machine Motion
Videopad video editor full free. Everything a machine can do is based on three basic types of motion:
- Rapid move: a linear move to an XYZ position as fast as possible
- Feed move: a linear move to an XYZ position at a defined feed rate
- Circular move: a circular move at a defined feed rate
Every g-code tells the machine which variation of these basic motions to perform, and how to perform it.
X and Y are Cartesian coordinates for horizontal and vertical position, and Z represents the depth of the machine. These alpha numerals will follow the motion/function command (G) to declare the position of the machine.
Next, F determines the feed rate (for feed moves or circular moves), while S determines the spindle speed. T is used to select a tool. Other alpha numerals used in programming might include I, J, and R, which have to do with arc centers and radii.
Miscellaneous Codes
The line of a program might also include m-codes, which are generally codes that tell a machine how to perform an action. While not guaranteed to be the same across machines, some common, standard m-codes are:
- M00: Program stop
- M01: Optional program stop
- M02: End of program
- M03: Spindle on clockwise
- M04: Spindle on counterclockwise
- M05: Spindle stop
- M06: Tool change
- M08: Flood coolant on
- M09: Flood coolant off
- M30: End of program/return to start
- M41: Spindle low gear range
- M42: Spindle high gear range
Modality
Just like a light will stay on until it’s turned off, g-code functions (on controllers that support modality) will remain active until they are deactivated by another code. In other words, only one function can be active at any given time. To deactivate a function, just select a new function.
For example, say a code begins with a linear rapid move at X1 Y1 (G00 X1 Y1). If the next function is another linear rapid move, it is not necessary to write G00 again. All that is needed on the next line of code is the new position (say, X2 Y2) because the modal condition is the same. Then, to change the function to a linear feed (G01), programming G01 on the following line would deactivate the linear rapid move and activate the linear feed.
Once a condition is set, it stays active until it is turned off or another condition overrides it.
Canned Cycles
Canned cycles are a kind of modal condition that incorporate all the motions to complete a common task into one code.
Mazak Cnc Lathe Programming Manual
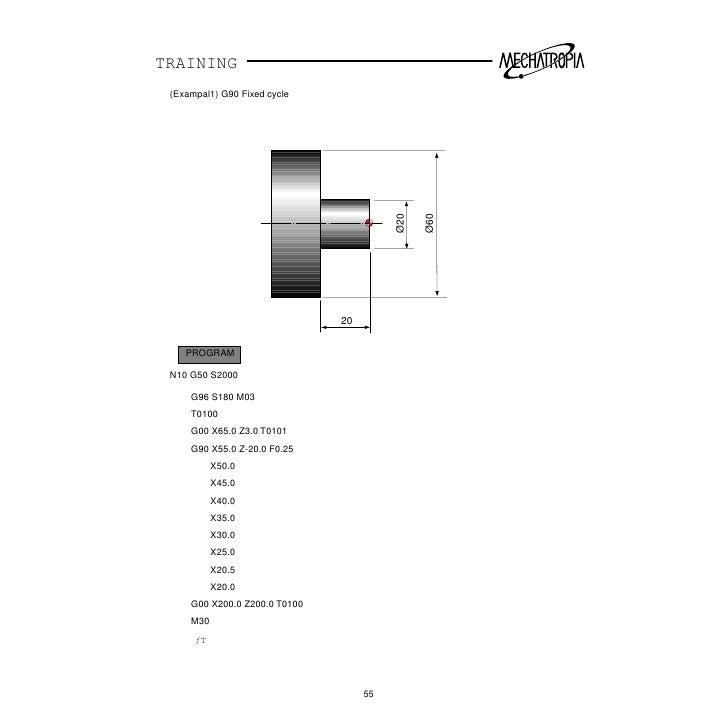
For example, oftentimes G81 is code for a basic drilling function. In the case of basic drilling, the tool would have to be 1) moved to the starting point of the hole’s location, 2) rapid to the clearance plane, 3) fed to the depth, and 4) rapid out. That would be four lines of code in the program that would have to be repeated for every new drill position! With the canned cycle G81, only the hole locations need to be specified after activation. Canned cycles like G81 significantly reduce the amount of code by incorporating multiple motions into one code.
Free Cnc Lathe Programming Software
Some other common canned cycles exist for peck drilling, counter boring, and tapping.